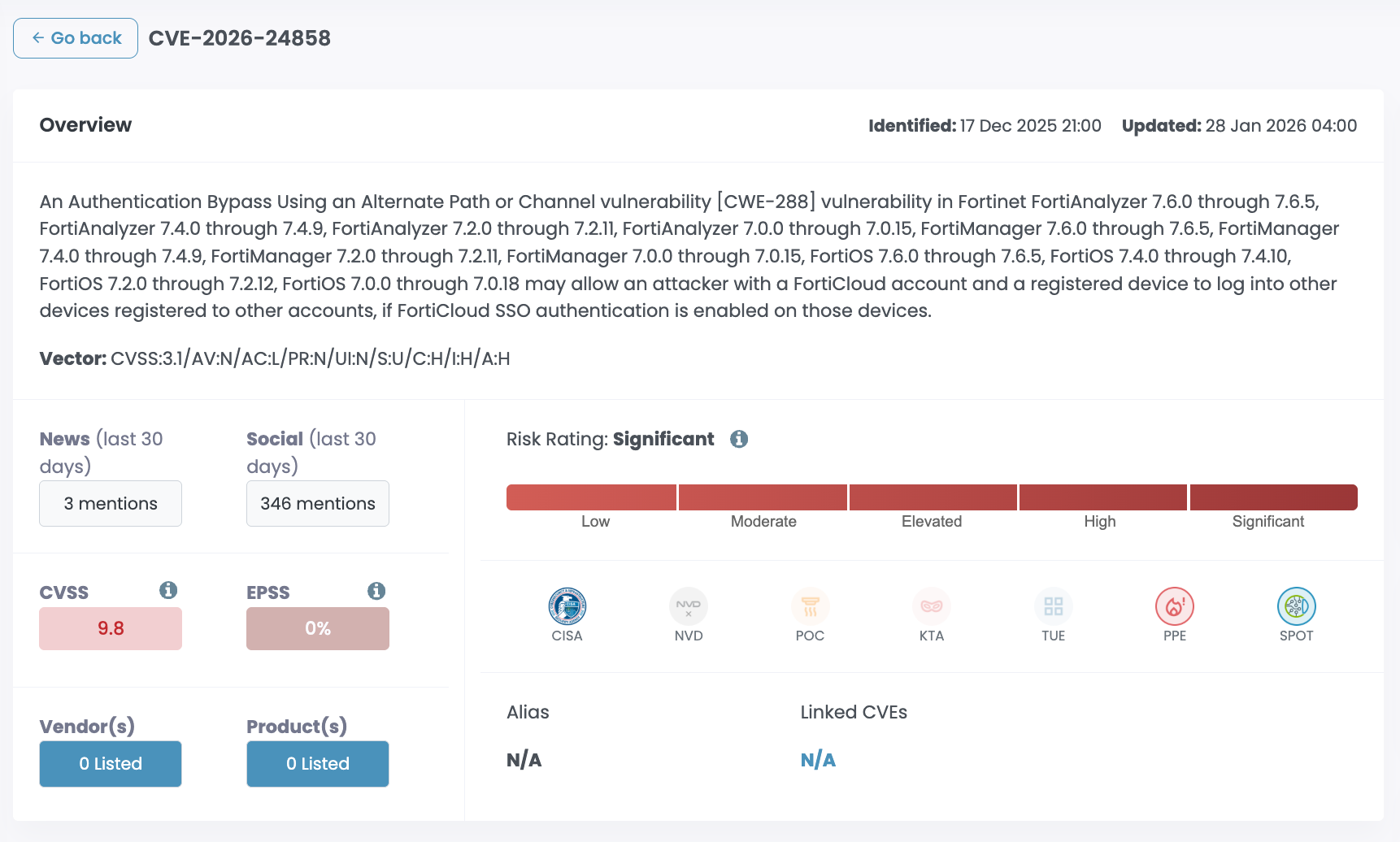
CVE-2026-24858: FortiCloud SSO Let Attackers Log Into Other Customers' Devices
CVE-2026-24858 exploited in the wild: FortiCloud SSO Let Attackers Log Into Other Customers' Devices
CVE-2026-24858 describes a critical authentication bypass vulnerability affecting multiple Fortinet products when FortiCloud Single Sign-On (SSO) is enabled for administrative access.
The vulnerability allows an attacker with a valid FortiCloud account and a registered device to log into other customers’ Fortinet devices if FortiCloud SSO is enabled on those targets.
This vulnerability has been actively exploited in the wild, confirmed by Fortinet. The assigned CVSSv3 score is 9.4 (Critical); vulnerability class: CWE-288 – Authentication Bypass Using an Alternate Path or Channel.
As an immediate response, Fortinet temporarily disabled FortiCloud SSO on January 26, 2026 and enforced upgrades as a prerequisite for authentication from January 27, 2026 onwards.
Default Configuration and Exposure Conditions
FortiCloud SSO administrative login is not enabled by default. Exposure typically occurs during device onboarding when:
- The administrator registers a device to FortiCare via the GUI
- If the option “Allow administrative login using FortiCloud SSO” is not manually disabled
- FortiCloud SSO becomes active unless explicitly disabled by the administrator
This increases real-world exposure where administrators leave the toggle enabled unintentionally.
Exploitation Status and Timeline
- In-the-wild exploitation confirmed by Fortinet
- Exploitation attributed to two malicious FortiCloud accounts, locked on January 22, 2026
- January 26, 2026: Fortinet disabled FortiCloud SSO
- January 27, 2026: SSO re-enabled, blocking vulnerable versions
- Login from devices running vulnerable firmware is now blocked until upgrade
Affected Products and Versions
Products Under Investigation
- FortiWeb
- FortiSwitch Manager
Confirmed Affected Products
FortiAnalyzer
|
Version |
Affected |
Solution |
|
7.6 |
7.6.0 – 7.6.5 |
Upgrade to 7.6.6 or above |
|
7.4 |
7.4.0 – 7.4.9 |
Upgrade to 7.4.10 or above |
|
7.2 |
7.2.0 – 7.2.11 |
Upgrade to 7.2.12 or above |
|
7.0 |
7.0.0 – 7.0.15 |
Upgrade to 7.0.16 or above |
|
6.4 |
Not affected |
N/A |
FortiManager
|
Version |
Affected |
Solution |
|
7.6 |
7.6.0 – 7.6.5 |
Upgrade to 7.6.6 or above |
|
7.4 |
7.4.0 – 7.4.9 |
Upgrade to 7.4.10 or above |
|
7.2 |
7.2.0 – 7.2.11 |
Upgrade to 7.2.13 or above |
|
7.0 |
7.0.0 – 7.0.15 |
Upgrade to 7.0.16 or above |
|
6.4 |
Not affected |
N/A |
FortiOS
|
Version |
Affected |
Solution |
|
7.6 |
7.6.0 – 7.6.5 |
Upgrade to 7.6.6 or above |
|
7.4 |
7.4.0 – 7.4.10 |
Upgrade to 7.4.11 or above |
|
7.2 |
7.2.0 – 7.2.12 |
Upgrade to 7.2.13 or above |
|
7.0 |
7.0.0 – 7.0.18 |
Upgrade to 7.0.19 or above |
|
6.4 |
Not affected |
N/A |
FortiProxy
|
Version |
Affected |
Solution |
|
7.6 |
7.6.0 – 7.6.4 |
Upgrade to 7.6.6 or above |
|
7.4 |
7.4.0 – 7.4.12 |
Upgrade to 7.4.13 or above |
|
7.2 |
All versions |
Migrate to a fixed release |
|
7.0 |
All versions |
Migrate to a fixed release |
Workarounds and Mitigations
Client-side disabling of FortiCloud SSO is not required currently, as service-side enforcement now blocks vulnerable versions.
However , for defense-in-depth, administrators may disable SSO locally as follows:
GUI Path:
System → Settings → Allow administrative login using FortiCloud SSO → Off
CLI Configuration:
config system global
set admin-forticloud-sso-login disable
end
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Observed FortiCloud SSO User Accounts
Note: These identifiers may change as response actions continue.
Observed IP Addresses (Fortinet)
- 104.28.244.115
- 104.28.212.114
- 104.28.212.115
- 104.28.195.105
- 104.28.195.106
- 104.28.227.106
- 104.28.227.105
- 104.28.244.114
Additional IPs Observed by Third Parties
- 37.1.209.19
- 217.119.139.50
Malicious Local Admin Account Names
- audit
- backup
- backupadmin
- deploy
- itadmin
- remoteadmin
- secadmin
- security
- support
- svcadmin
- system
Observed Attacker Operations
- Downloading device configuration files
- Creating local administrator accounts to maintain persistence
Risk Assessment
- Likelihood: High
- Impact: Critical
- Exploit Status: Confirmed in-the-wild exploitation
- Attack Prerequisite: FortiCloud account with a registered device
Compromise of affected devices enables administrative control over security infrastructure, creating significant downstream risk.
Cytidel Recommendations
- Immediately upgrade all affected Fortinet products to fixed versions
- Validate FortiCloud SSO configuration during device registration workflows
- Review authentication logs for IOC-listed accounts and IPs
- Audit all local administrator accounts for unauthorized creation
- Treat any confirmed compromise as a full device breach and rotate credentials

![[Updated] Four 9.8s in SolarWinds Web Help Desk: Why We're Flagging This Before Exploitation Hits](/content/images/size/w600/2026/01/solarwinds.png)


